SQLite. It’s the little database that could, quietly powering countless applications, from your smartphone to your web browser. It's famed for its simplicity, zero-configuration setup, and impressive performance, all within a single file. But for many, SQLite's single-file nature has been its biggest limitation. What if you could leverage SQLite's power in more distributed, scalable scenarios? That's where a fascinating wave of projects comes in, promising a new era for SQLite.
The Distributed SQLite Landscape: A Quick Overview
Litestream: Perhaps the most well-known, Litestream provides real-time replication of SQLite databases to cloud storage (like S3 or Backblaze B2). It essentially transforms your SQLite file into a stream of changes that can be replayed on other servers, enabling read replicas and even basic failover.
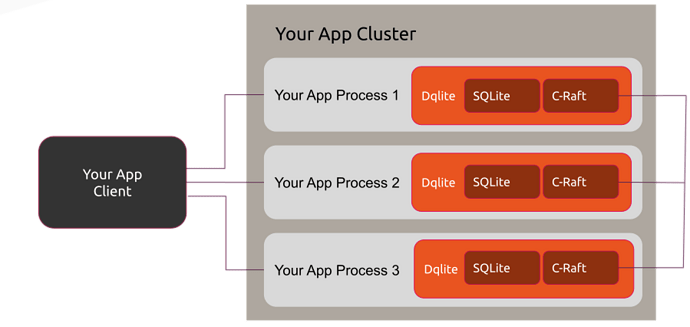
dqlite: Developed by Canonical, dqlite provides a distributed version of SQLite using an Raft consensus algorithm. This allows for strong consistency and fault tolerance, making it suitable for more critical applications. While it requires a bit more setup than Litestream, it offers a robust distributed database solution.
rqlite: Similar to dqlite, rqlite also employs Raft for consensus but focuses on ease of use and operational simplicity. It aims to be a lightweight, reliable distributed database that is easy to deploy and manage.
LiteFS: Designed specifically for edge computing environments, LiteFS replicates SQLite databases using a simple file system synchronization mechanism. This makes it extremely efficient and suited for scenarios where low-latency reads are paramount, such as global deployments.
The Allure of Distributed SQLite
Why are these projects gaining so much traction? It comes down to a few key factors:
Costs: Many of these distributed SQLite options are designed to run on simple VMs or containers. Litestream, for example, can replicate directly to low-cost cloud object storage. This translates to a significantly lower infrastructure footprint compared to running traditional database clusters.
Operational: These systems generally aim for ease of setup and maintenance. You don't need a dedicated database administrator team to handle the intricacies of a distributed SQLite system. This translates to less time managing the underlying database and more time building your application.
Simplicity: SQLite is renowned for its ease of use. These distributed solutions strive to maintain that simplicity, abstracting away much of the complexity inherent in distributed systems.
Efficiency: SQLite's embedded nature makes it very efficient in resource usage. These solutions aim to bring that efficiency to distributed environments, resulting in lower operational costs and reduced overhead.
Scalability (with caveats): While these solutions might not be suitable for write-heavy applications requiring extreme horizontal scaling, they allow SQLite to extend beyond a single machine, providing more flexibility for many use cases.
Edge Computing & IoT: The lightweight nature and simplicity of SQLite make it a perfect fit for edge devices. Distributed versions open up new possibilities for data synchronization and replication in these environments.
Predicting Growth in the Year Ahead
The distributed SQLite movement is just getting started, and I predict it's going to be a major trend to watch in the coming year. Here's what I see unfolding:
Increased Adoption: As more developers discover the potential of these projects, we'll see wider adoption across various application types.
Maturity and Stability: The projects are constantly evolving, and we can expect to see them become more stable and feature-rich in the coming months.
Focus on Developer Experience: Simplified deployment, intuitive APIs, and better tooling will be crucial to drive adoption, and I expect to see more focus on improving developer experience.
Cloud Integration: Expect closer integration with popular cloud platforms, making it easier to deploy and manage distributed SQLite setups.
Edge Computing Dominance: The unique combination of low resource usage, simplicity, and offline capabilities positions distributed SQLite to be a key technology for edge computing and IoT scenarios.
More Use Cases: As more developers explore the landscape we will see a plethora of new use cases for distributed sqlite.
The Future is Distributed (And Possibly SQLite)
SQLite's journey is far from over. Its foray into distributed systems marks a new chapter for this beloved database. These technologies are not designed to replace fully fledged distributed database, but instead offer a compelling alternative in the space of embedded, edge or less demanding distributed scenarios. While there are limitations to its use, the promise of simple, efficient, and reliable distributed data management is undeniable. Whether you're building a web application, an edge computing solution, or an IoT project, exploring distributed SQLite might just unlock new possibilities you hadn't considered. The coming year promises to be an exciting time for this emerging field. Keep an eye out – it's a revolution in the making!